The mesh of a fluid simulation describes the points where the flow equations are solved. The stability and the precision of the calculations depend strongly on the mesh
type and quality.
The conjugated heat transfer is the mutual influence of the temperature fields of the solids and the flow; these must be calculated here
simultaneously; the grid must also include both the fluid and the solids.
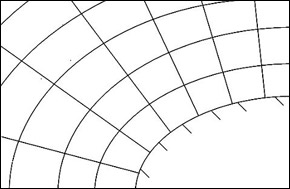
Structured grids have a regular topology; the cells are placed regularly so that the cells can be indexed with integer numbers.
In order for the grid
to be adapted to the geometry, the grid lines must follow the body geometry.
In order to generate the mesh of the fluid parts, a negative geometry, which comprises the whole volume between the solid parts, must first be
generated. This volume will be split into smaller domains, the so-called cells. When a high-quality mesh is required, then a full hexahedral mesh is
the best option. The calculation domain is first of all divided into blocks; these blocks are later split into hexahedrons by
the meshing tool.
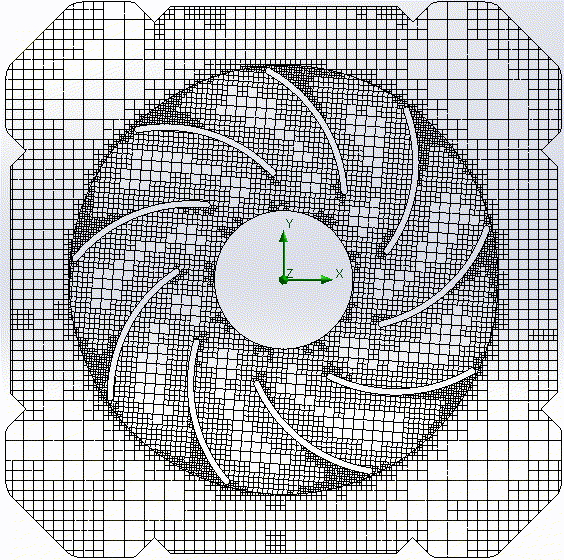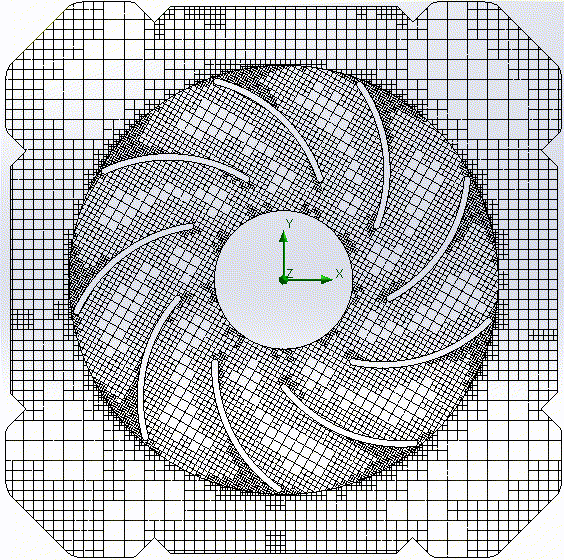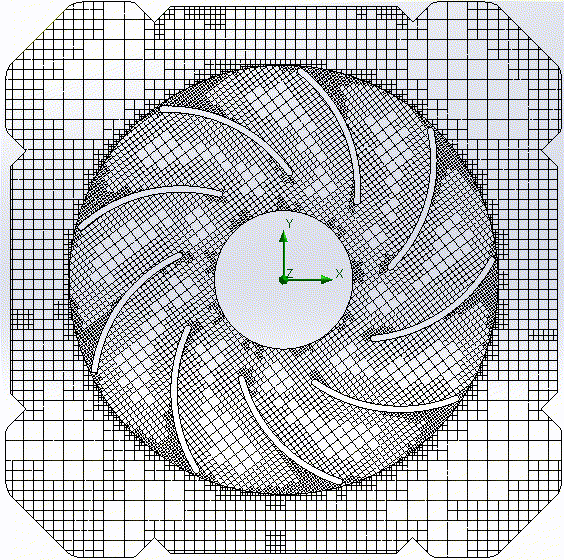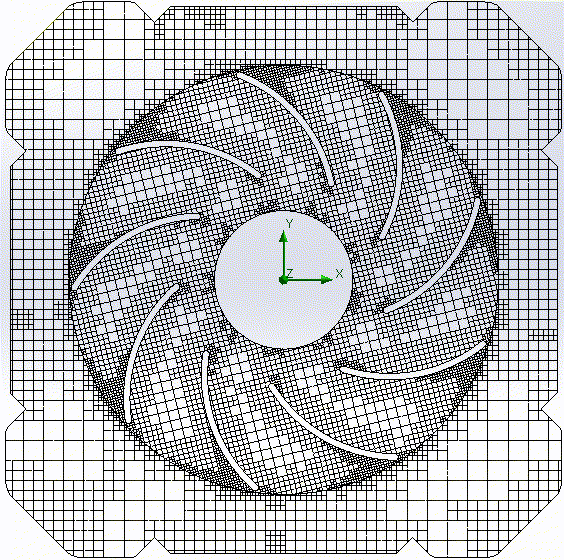
 Geometry-fitted mesh with hexaeders |
 Geometry-fitted unstructured tetraeders |
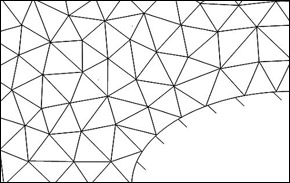
Also commonly used since 2000 are mesh generation tools which are based on unstructured mesh, with triangles (in 2D) or tetrahedrons (in 3D). The
program primarily generates automatic cells which are fitted to the surfaces. For complex geometries, it is quite difficult and time-consuming
to generate a good tetrahedral mesh as the generation of strongly distorted cells can hinder the convergence of the calculation. The user must therefore
manually choose the correct parameters in order to generate a good mesh.
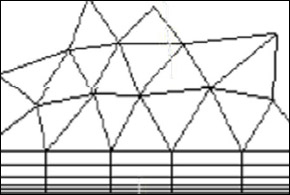
It is common practice to mesh with hexahedrons close to the walls and with tetrahedrons elsewhere, in order to solve the boundary layer with
extremely thin cells.
 Mixed structured hexaeder and unstructured tetraeder mesh |
 Cartesian mesh |
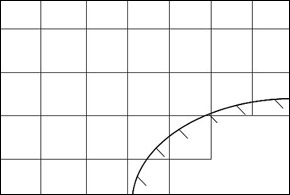
Cartesian meshes are the right alternative to geometry fitted meshes. CFD
Tools using this mesh type like FloEFD, FloTherm or Solidworks Flow Simulation offer more precise and efficient
algorithms. Here you do not need to create a model of the fluid region like in
the classical approach; the tool recognizes the fluid region based on the
empty spaces between the solid geometries and the location of the boundary regions.
The geometry bodies are immersed in the cartesian mesh. The mesh lines no longer fit to the bodies of complex geometries. In locations where the
boundaries of the bodies do not fit to the cartesian mesh, interpolations must be used in order to take into account the effects of the misalignment between
mesh and geometry. The cartesian mesh allows the use of more efficient solving-algorithms despite this interpolation.
With this method, called Immersed Boundary Method, it is easier to simulate complex geometries as the cartesian mesh always remains and the body is simply immersed in the mesh.